How to Choose the Right Flow Control Valve for Your Application Needs
Choosing the right flow control valve for your application is a crucial decision that can significantly impact the efficiency and performance of your system. A flow control valve plays a vital role in regulating the flow of fluids within various industrial processes, ensuring that operations run smoothly and safely. With an array of options available on the market, understanding the specific requirements of your application is essential for making an informed choice.
When selecting a flow control valve, several factors must be considered, including the type of fluid, system pressure, and desired flow rate. The correct valve can enhance control over the fluid dynamics, providing benefits such as energy savings, improved process stability, and reduced operational costs. Conversely, an unsuitable flow control valve can lead to complications, such as pressure drops, flow disruptions, or even system failures. Therefore, gaining insights into different valve types, materials, and ratings is necessary for optimizing your application’s performance and ensuring longevity.
In this article, we will explore the key aspects to consider when choosing a flow control valve, arming you with the knowledge to make a sound decision that aligns with your operational needs. From understanding the fundamental principles of flow control to evaluating specific valve characteristics, this guide will help streamline your selection process and support your goals for operational excellence.

Understanding Flow Control Valves: Types and Functions
Flow control valves are essential components in various systems, designed to manage the rate and direction of fluid flow. Understanding the different types of flow control valves is crucial for selecting the right one for your specific application. The main types include gate valves, globe valves, ball valves, and check valves, each serving distinct functions. Gate valves, for instance, are primarily used to start or stop flow, functioning well in high-pressure applications but not suitable for throttling. Globe valves provide better flow regulation and are ideal for applications where flow needs to be constantly adjusted.
In addition to type, the function of the flow control valve plays a significant role in optimizing system performance. For instance, a throttle valve is designed specifically to manage flow rates and can be found in applications like hydraulic systems, where precise control is necessary for operational efficiency. Conversely, a pressure relief valve is critical for protecting systems from overpressure, ensuring safety and reliability. Selecting the appropriate valve requires a comprehensive understanding of the operational environment, desired flow characteristics, and potential system constraints, guaranteeing that the chosen valve meets the operational demands.
How to Choose the Right Flow Control Valve for Your Application Needs - Understanding Flow Control Valves: Types and Functions
| Valve Type | Function | Application Areas | Material | Size Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Globe Valve | Flow regulation and throttling | Water supply, HVAC, and chemical processing | Cast iron, stainless steel | 1/2" to 12" |
| Ball Valve | On/off control with minimal flow restriction | Oil and gas, water treatment | Brass, PVC, stainless steel | 1/4" to 24" |
| Butterfly Valve | Flow regulation with a rotating disk | Water distribution, wastewater management | Aluminum, ductile iron, stainless steel | 2" to 48" |
| Check Valve | Prevent backflow in piping systems | Pumping stations, irrigation systems | Bronze, PVC, stainless steel | 1" to 16" |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Maintain set pressure by releasing excess pressure | Boiler systems, chemical plants | Stainless steel, carbon steel | 1/2" to 10" |
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Flow Control Valve
When selecting a flow control valve for your application, it’s essential to consider several key factors to ensure optimal performance. First, assess the fluid characteristics, including viscosity, temperature, and corrosiveness. Understanding the nature of the fluid is crucial, as different materials and valve types react differently to various fluids. Additionally, consider the flow rate requirements of your application; knowing the desired flow rate helps in choosing a valve that can efficiently meet your system's demands.
Another important aspect is the valve's pressure rating, which should be compatible with the system's operating pressure. Selecting a valve with a pressure rating that exceeds your application’s maximum operating pressure will enhance safety and reliability. Additionally, the size and connection type of the valve must match your existing piping system to avoid any installation issues.
Tips:
- Always consult with engineering guidelines or flow charts to identify the appropriate valve type based on your specific application.
- Keep in mind the environment where the valve will be used. If it's exposed to extreme conditions, such as high temperatures or corrosive environments, opting for specialized materials can extend its lifespan.
- Evaluate the ease of maintenance and accessibility when selecting a valve to ensure that future servicing does not become a challenging task.
Assessing Compatibility with Fluid Properties and System Requirements
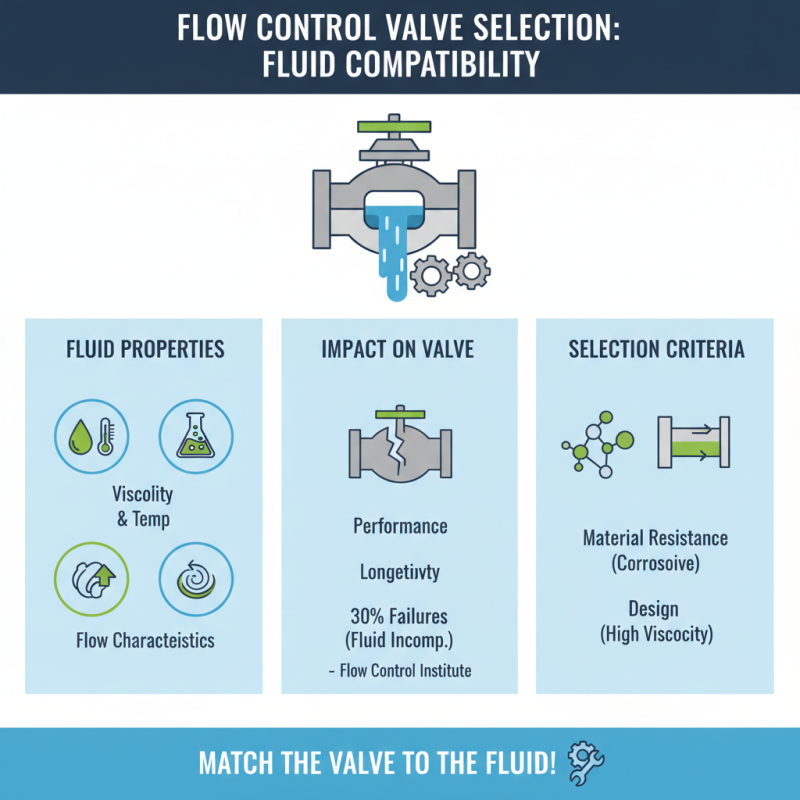
When selecting a flow control valve, one of the critical factors to consider is the compatibility with the fluid properties involved in your application. Each fluid has unique characteristics, such as viscosity, temperature, and chemical composition, which can significantly impact the performance and longevity of the valve. According to a report by the Flow Control Institute, approximately 30% of flow control valve failures can be attributed to incompatibility with the fluid. For example, corrosive fluids require materials that can withstand chemical reactions, while highly viscous fluids may necessitate valves designed for increased flow resistance to maintain operational efficiency.
In addition to fluid properties, evaluating system requirements is equally essential. Factors such as pressure ratings, flow rates, and environmental conditions must align with the specifications of the flow control valve to ensure optimal functionality. According to the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), improperly rated valves can lead to a 25% increase in energy consumption over the operational lifespan. Understanding the operational environment will guide engineers in choosing the right valve configuration, such as globe valves for throttling applications or ball valves for on-off control, allowing for better system integration and enhanced performance.
Evaluating Flow Rate and Pressure Drop for Optimal Performance
When selecting the appropriate flow control valve for a given application, evaluating the flow rate and pressure drop is crucial for ensuring optimum performance. According to a report from the International Society of Automation, a significant factor influencing valve efficiency is the relationship between flow rate and pressure drop across the valve. For instance, a well-designed control valve should maintain a flow rate within 5-25% of its maximum capacity while minimizing pressure drop to ensure energy efficiency and system stability.
 The flow characteristics of various valve types can significantly impact system performance. A recent study published in the Journal of Fluid Engineering highlights that control valves optimized for lower pressure drops can enhance the overall efficiency of a fluid system by up to 30%. When dealing with high-pressure systems, selecting valves designed for minimal cavitation can further reduce pressure loss and improve flow consistency. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements of the fluid—such as viscosity and density—can guide engineers in choosing the right size and type of valve, which is essential for maintaining optimal operational performance and meeting safety standards.
The flow characteristics of various valve types can significantly impact system performance. A recent study published in the Journal of Fluid Engineering highlights that control valves optimized for lower pressure drops can enhance the overall efficiency of a fluid system by up to 30%. When dealing with high-pressure systems, selecting valves designed for minimal cavitation can further reduce pressure loss and improve flow consistency. Additionally, understanding the specific requirements of the fluid—such as viscosity and density—can guide engineers in choosing the right size and type of valve, which is essential for maintaining optimal operational performance and meeting safety standards.
Installation and Maintenance Tips for Flow Control Valves
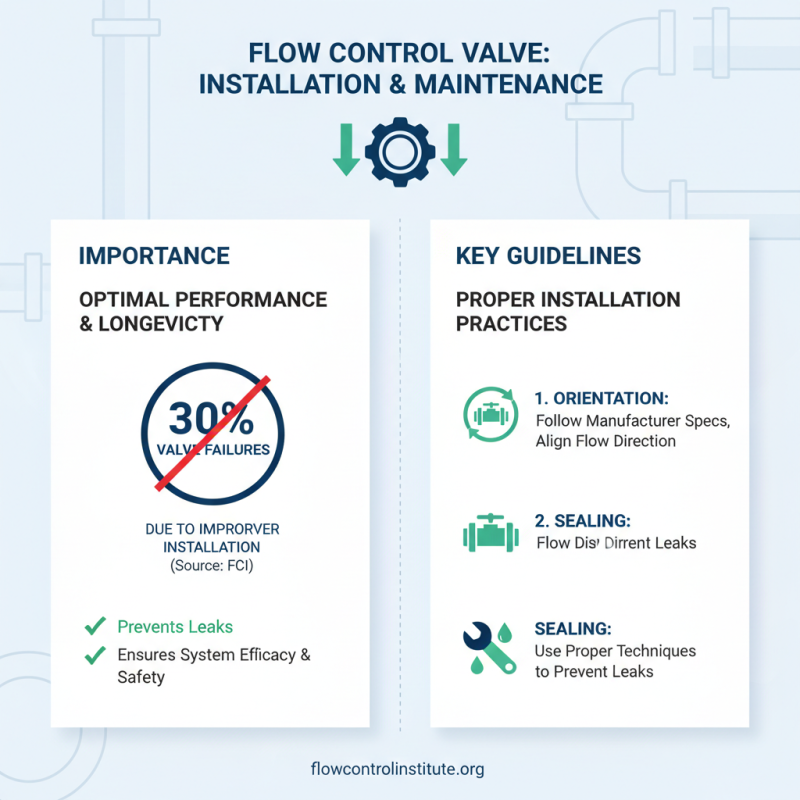
When it comes to flow control valves, proper installation and maintenance are crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity. According to the Flow Control Institute (FCI), nearly 30% of industrial valve failures can be attributed to improper installation practices. Therefore, it is essential to follow specific guidelines when installing these valves. The orientation of the valve should be consistent with the manufacturer’s specifications, ensuring that flow direction indicators are aligned correctly. Additionally, proper sealing techniques must be employed to prevent leaks, which can significantly impact system efficacy and safety.
Regular maintenance is equally important in prolonging the life of flow control valves. The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) suggests implementing a routine inspection schedule to check for wear and tear, particularly in high-pressure applications. Regularly monitoring valve performance metrics, such as flow rate and response time, can help identify any potential issues before they lead to failure. Furthermore, utilizing diagnostic tools can enhance maintenance strategies by providing real-time data on valve performance, ensuring that any necessary adjustments or replacements are made promptly. By adhering to these installation and maintenance practices, users can significantly reduce downtime and enhance the efficiency of their fluid control systems.
Related Posts
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Flow Check Valve for Your System Needs
-

Understanding the Importance of Relief Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

Exploring the Innovations and Technologies Shaping the Future of Ball Valve Manufacturers
-

Top 10 Check Valve Types for Optimal Flow Control and Industry Applications
-

Understanding the Benefits of Choosing Stainless Ball Valves for Your Plumbing Needs
-

Understanding the Importance of Safety Valves in Preventing Industrial Accidents and Ensuring Compliance
