How to Choose the Right Control Valve for Your Industrial Applications
When it comes to optimizing industrial processes, one crucial component that often determines the efficiency and effectiveness of operations is the control valve. Control valves serve as the linchpin in a myriad of applications, regulating flow, pressure, and temperature in various systems. Selecting the appropriate control valve is not merely a matter of preference; it requires meticulous consideration of several factors tailored to the specific industrial environment. Whether in oil and gas, chemical manufacturing, or HVAC systems, the right control valve can significantly impact overall performance, safety, and reliability.
Understanding the different types of control valves and their functionalities is essential for making an informed decision. Factors such as the nature of the media being controlled, operating conditions, and system requirements all play a significant role in determining the ideal valve type. Furthermore, one must also consider aspects like maintenance needs, installation considerations, and the compatibility of materials used in valve construction.
As industries continue to evolve and demand higher efficiency and precision, the importance of selecting the right control valve cannot be overstated. This guide will delve into the key considerations and best practices in choosing the most suitable control valve for your specific industrial applications, ensuring effective management of your processes and ultimately leading to greater operational success.
Understanding the Role of Control Valves in Industrial Systems
Control valves are critical components in industrial systems, playing a vital role in regulating fluid flow and ensuring operational efficiency. They are designed to respond dynamically to changes in process conditions, such as pressure, temperature, and flow metrics. According to a report by the International Society of Automation, inefficient control valve selection can lead to plant-wide inefficiencies, costing industries up to 30% of their operational expenses. Properly chosen control valves help maintain process stability, enhance system performance, and optimize energy usage.
When selecting a control valve, it's essential to understand the specific requirements of your application. Factors to consider include the type of fluid being controlled, pressure and temperature ranges, and the valve's control characteristics. For instance, utilizing the correct sizing and actuator type can significantly improve response times and reduce energy consumption.
Tips: Always conduct a thorough analysis of your system requirements prior to selecting a control valve. Consider utilizing software tools for valve sizing, as they can help identify the best options for your specific conditions. Regular maintenance checks and performance evaluations are crucial in ensuring that your control valves operate at peak efficiency, ultimately improving the lifespan of your industrial system. Additionally, incorporating smart control technology can lead to better decision-making and real-time adjustments in valve operations.
Identifying Key Factors for Selecting Control Valves
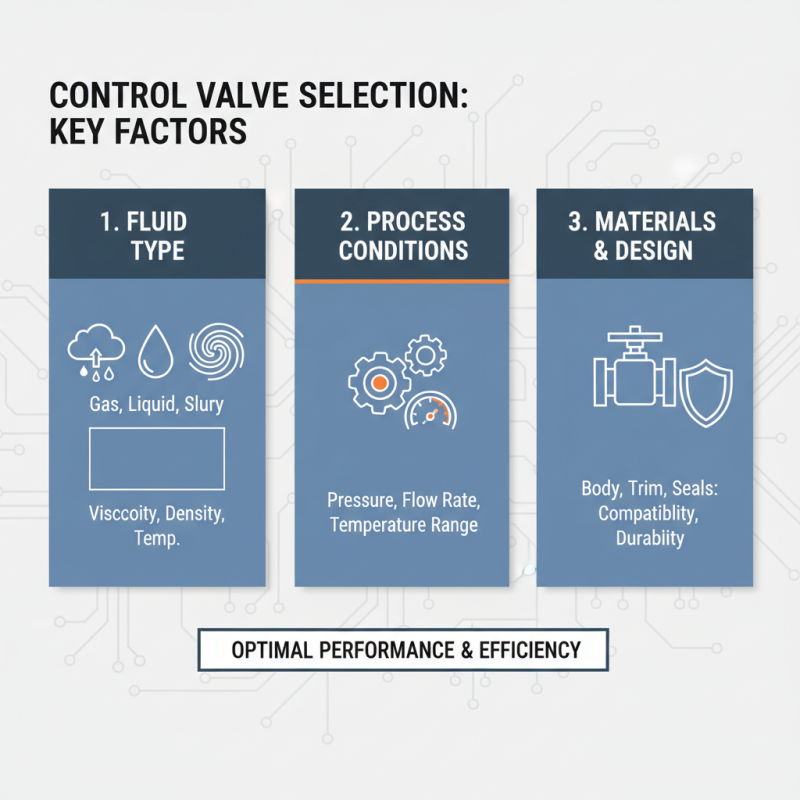
When selecting the right control valve for industrial applications, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. First, the type of fluid being controlled plays a crucial role. Different fluids, whether they are gases, liquids, or slurries, have varying physical properties such as viscosity, density, and temperature. Understanding these characteristics helps determine the appropriate valve type and materials to avoid corrosion or wear that could affect long-term functionality.
Another important factor is the pressure and temperature conditions of the application. Valves must be rated to handle the specific operating pressures and temperatures they will encounter in service. Operators should also consider the flow characteristics required, such as direct or throttling flow control, since this will influence the valve design and sizing. Additionally, the control methodology—whether manual, pneumatic, or electric—will affect the choice of actuator and the overall compatibility with existing systems. By thoroughly assessing these parameters, industry professionals can choose control valves that enhance system performance and reliability.
Types of Control Valves and Their Applications
When selecting a control valve for industrial applications, understanding the types and their specific uses is crucial for efficiency and safety. Control valves can be categorized into several types, including globe valves, ball valves, butterfly valves, and solenoid valves. Each type serves different purposes based on the application's requirements. For instance, globe valves are excellent for throttling flow and providing precise control, making them suitable for processes requiring close regulation. In contrast, ball valves offer superior sealing capabilities and are ideal for on/off control, particularly in high-pressure and high-temperature scenarios.
Tips: When choosing a control valve, always consider the fluid type, pressure, and temperature of your application. Additionally, think about the required response time and the valve's duty cycle. Proper sizing and selection based on the system's parameters can significantly impact performance and longevity.
Butterfly valves are commonly used in situations where quick shut-off is essential, and they are appreciated for their lightweight design and space-saving features. Solenoid valves, on the other hand, are preferred in automated systems for their rapid response time and ability to control high flows with minimal power consumption. Ultimately, the right choice of control valve depends on the specific criteria of your application and operational objectives, ensuring enhanced productivity and reliability.
How to Choose the Right Control Valve for Your Industrial Applications - Types of Control Valves and Their Applications
| Control Valve Type | Application | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ball Valve | On/off control in pipelines | Quick opening and closing, low friction | Not suitable for throttling |
| Globe Valve | Flow regulation and throttling | Good flow control, can handle high pressures | Higher pressure drop, slower operation |
| Butterfly Valve | Large volume control | Lightweight, compact size, quick operation | Limited throttling capability |
| Gate Valve | On/off applications | Minimal pressure drop, full flow when open | Slow operation, not suitable for throttling |
| Pressure Relief Valve | Safety applications in pressure vessels | Protects system from overpressure | Needs regular maintenance |
Evaluating Valve Materials and Specifications
When selecting the right control valve for industrial applications, evaluating valve materials and specifications is critical to ensuring optimal performance and longevity. The choice of materials directly influences the valve's ability to withstand various environmental conditions, including temperature extremes, pressure fluctuations, and potential exposure to corrosive substances.
According to a recent industry report by the Valve Manufacturers Association, nearly 40% of valve failures in petrochemical plants are attributed to incompatible materials, emphasizing the importance of a thorough materials assessment.
Commonly used materials for control valves include stainless steel, carbon steel, and various alloys, each suited for specific applications. Stainless steel, for instance, offers excellent resistance to corrosion and is ideal for high-purity applications, while carbon steel is often preferred in standard pressure and temperature scenarios due to its cost-effectiveness. A study conducted by the International Society of Automation found that the right material selection could increase operational efficiency by up to 25%, highlighting the substantial impact of material choice on industrial performance.
In addition to material compatibility, understanding the specifications of the control valves—such as flow coefficient (Cv), end connections, and actuator types—is equally important. The Cv value indicates the flow capacity of the valve, which should align with the requirements of the application to optimize flow rates and avoid pressure drops. A well-informed selection process, grounded in a solid evaluation of materials and specifications, not only enhances the reliability of the system but also contributes to reduced maintenance costs and improved safety in industrial environments.
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Control Valves in Industries
Maintaining and troubleshooting control valves is crucial for ensuring operational efficiency in industrial applications. Regular maintenance helps prevent unexpected downtime and costly repairs. Operators should routinely inspect control valves for signs of wear, corrosion, or leaks. It is essential to check the actuator performance, as it directly affects valve responsiveness. Keeping the valve body and associated piping clean can significantly improve flow characteristics and prevent blockages that may hinder performance.
When troubleshooting control valves, it is important to diagnose common issues such as erratic valve behavior, vibrations, or oscillations. Operators should systematically evaluate the control system response and confirm that the valve is receiving appropriate signals. Adjustments to the actuator or replacing worn components may be required for optimal performance. Implementing a preventive maintenance program that includes regular testing, calibration, and documentation of valve operation can greatly enhance reliability and extend the lifespan of control valves in various industrial settings.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Importance of Control Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

Unlocking Opportunities for Vacuum Check Valves at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Pressure Vacuum Valves in Modern Industrial Systems
-

Top 10 Essential Valve Tags for Efficient Industrial Safety Management
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Flow Check Valves in Your Plumbing System
-

Top 10 Hydrogen Valves for Optimal Performance and Safety in Applications
