Why Choosing the Right Pressure Relief Valve is Essential for Safety and Efficiency
In today's industrial landscape, the significance of selecting the appropriate pressure relief valve cannot be overstated, as it is pivotal for ensuring both safety and operational efficiency. According to a report by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), approximately 30% of industrial accidents are attributed to equipment failures, many of which could have been mitigated with the appropriate safety measures, including the proper functioning of pressure relief valves. These essential components are designed to prevent over-pressurization in systems, safeguarding not only equipment but also personnel and the surrounding environment.
Moreover, a comprehensive study by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) highlights that incorrect sizing or selection of pressure relief valves is a leading cause of system inefficiency. Properly sized and selected valves can optimize processes, reduce waste, and significantly lower operational costs. In fact, organizations that implement best practices in the selection of pressure relief valves see an average of 15% improvement in system reliability. Thus, understanding the critical role that pressure relief valves play in industrial operations is essential for any organization looking to enhance both safety protocols and efficiency metrics.
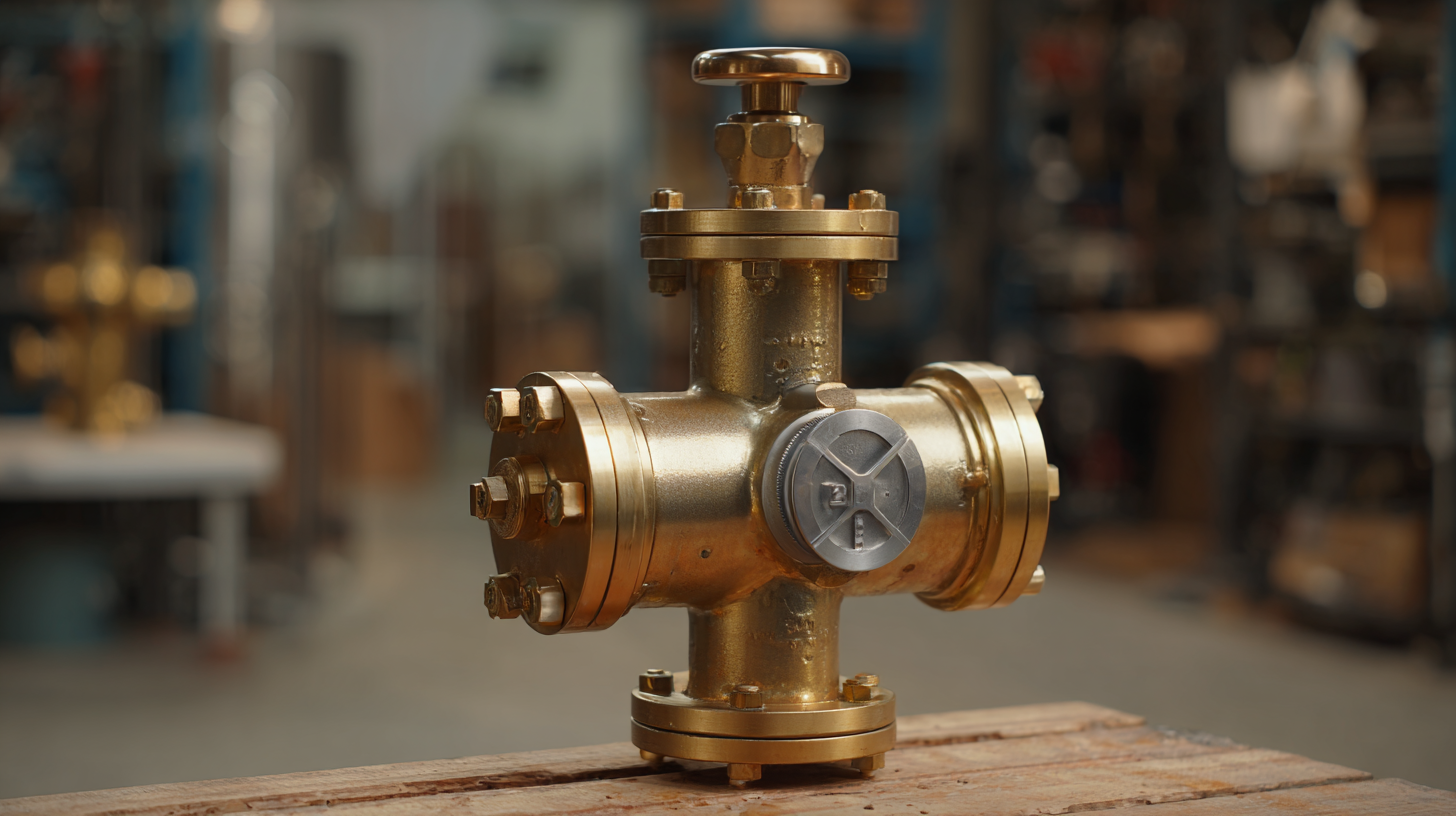

Understanding the Role of Pressure Relief Valves in Industrial Safety
Pressure relief valves (PRVs) play a pivotal role in industrial safety, acting as the last line of defense against overpressure conditions. According to a report by the Safety Engineering Institute, approximately 50% of industrial accidents are related to pressure vessel failures, often leading to catastrophic consequences. Properly functioning PRVs can mitigate these risks by releasing excess pressure, thereby preventing equipment failure and potential hazards to personnel.
When selecting a PRV, it’s essential to consider not only the pressure ratings but also the specific application to ensure optimal performance. An analysis from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) emphasizes that a miscalibrated valve can result in unnecessary downtime and increased operational costs. To maintain safety and efficiency, regular maintenance and testing of PRVs are crucial.
**Tips:** Regularly review and calibrate your pressure relief valves based on the manufacturer's guidelines to avoid malfunction. Additionally, train your team on recognizing signs of valve wear or failure to keep your operation safe and efficient. Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule can significantly extend the lifespan of your safety devices while promoting compliance with industry standards.
Pressure Relief Valve Performance in Different Industries
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Pressure Relief Valve
When selecting a pressure relief valve (PRV), several key factors must be considered to ensure both safety and operational efficiency. One of the most critical aspects is the valve’s set pressure, as it directly impacts the system's ability to relieve excess pressure. According to industry standards, such as those outlined by the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), the set pressure must be carefully determined based on the maximum allowable working pressure of the system, typically aligning with a safety margin of approximately 10%.
Another important consideration is the valve material and design, which must be compatible with the fluid being handled. For example, corrosive substances may require valves made of specialized materials such as Hastelloy or titanium to prevent premature failure. Reports indicate that improper material selection can lead to up to a 40% increase in maintenance costs over the lifespan of a facility, emphasizing the importance of choosing the right materials for longevity and safety.
Lastly, the flow capacity of the PRV should match the requirements of the system to prevent hazardous pressure build-up. Engineers often rely on flow rate equations and manufacturer specifications to ensure proper sizing. A report from the Chemical Engineering Research journal indicates that incorrect sizing of pressure relief valves accounts for nearly 30% of equipment failures in process industries, underscoring the critical nature of these selection factors in enhancing safety and efficiency.
Why Choosing the Right Pressure Relief Valve is Essential for Safety and Efficiency
| Factor | Description | Importance | Example Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure Setting | The predetermined pressure at which the valve will open to relieve excess pressure. | Critical for preventing overpressure scenarios. | Boiler systems, gas pipelines. |
| Material Selection | The choice of materials affects durability and resistance to corrosion. | Vital for longevity and cost-effectiveness. | Chemical processing, water treatment facilities. |
| Sizing | Proper sizing ensures the valve can handle the flow requirements. | Essential for efficiency and safety. | Oil & gas, power generation. |
| Code Compliance | Ensure that the chosen valve meets local regulations and standards. | Critical for legal and operational safety. | Manufacturing, commercial HVAC systems. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Evaluate how often the valve will need to be inspected or serviced. | Important for minimizing downtime and costs. | Food processing, pharmaceuticals. |
Common Types of Pressure Relief Valves and Their Applications
Pressure relief valves (PRVs) are crucial components in various industrial applications, designed to prevent excessive pressure buildup that can lead to catastrophic failures. Among the common types of PRVs, the spring-operated valve is the most widely used. It functions by employing a spring that holds the valve closed until the system pressure exceeds a predetermined limit, thus ensuring safe operation. These valves are typically found in applications such as boiler systems and chemical processing plants, where maintaining pressure within safe limits is critical.
Another prevalent type is the pilot-operated pressure relief valve, which offers enhanced sensitivity and control. This design utilizes a smaller pilot valve that controls the larger main valve, allowing for more precise regulation of pressure. Pilot-operated valves are ideal for high-pressure applications, including gas pipelines and refineries, where maximizing efficiency while minimizing the risk of overpressure is essential. Understanding the specific type and application of PRVs is vital for industries to ensure both safety and operational efficiency.
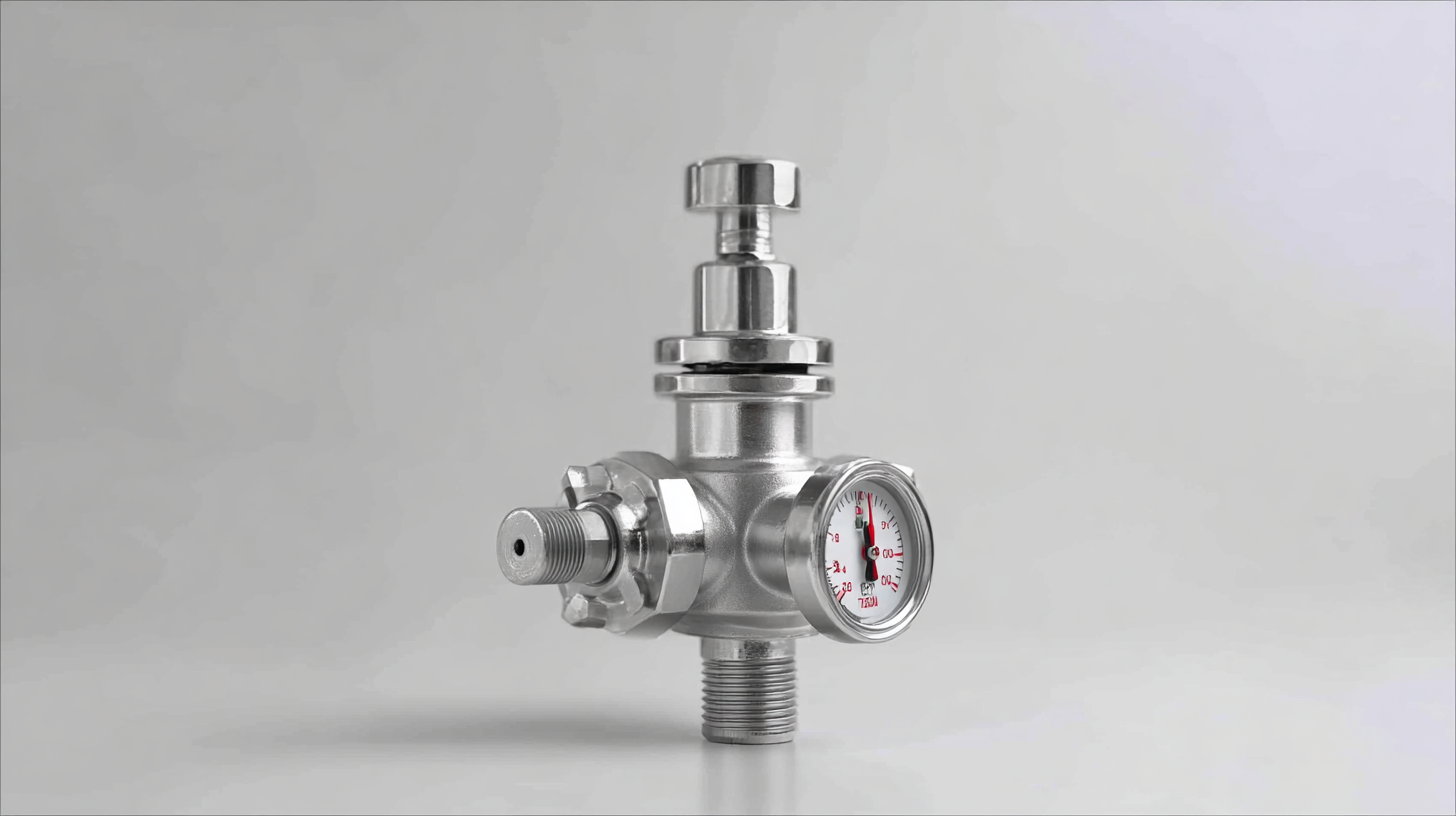

The Impact of Proper Valve Maintenance on System Efficiency
Proper maintenance of pressure relief valves is crucial for maintaining system efficiency, particularly in environments subjected to extreme conditions, such as dry climates, which can affect boiler performance. Regular inspection and servicing ensure that these valves operate without friction, preventing potential safety hazards that arise from valve malfunction. A valve's reliability is paramount; when maintenance is neglected, friction can build up, leading to decreased performance and even catastrophic failures in critical systems.

Tips for effective valve maintenance include scheduling routine inspections to identify wear and tear before it becomes a problem. Additionally, ensure that the seals and O-rings are in good condition to minimize friction and improve the efficiency of the valve's operation. Monitoring system pressure levels can also provide early warnings of potential issues, allowing for proactive maintenance interventions that enhance both safety and efficiency in industrial applications. Maintaining proper operation not only prolongs the life of your valves but significantly contributes to overall system reliability.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance for Pressure Relief Systems
The selection of an appropriate pressure relief valve is critical not only for operational efficiency but also for ensuring compliance with regulatory standards that govern industrial safety. Various organizations, such as the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) and the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), have established stringent guidelines to mitigate the risks associated with overpressure scenarios. These regulations dictate specific requirements for valve design, testing, and installation, which are essential to prevent catastrophic failures.
Compliance with these regulatory standards is not merely a legal obligation; it serves as a framework for maintaining safety and reliability within pressure relief systems. Organizations that adhere to these guidelines demonstrate a commitment to best practices, minimizing both environmental impact and the potential for hazards to personnel. By ensuring that the selected pressure relief valves meet or exceed the established criteria, industries can effectively safeguard their operations, enhancing overall efficiency while prioritizing safety.
Related Posts
-

Innovative Trends in Low Pressure Relief Valves at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-
Essential Guide to Understanding High Pressure Relief Valves: How They Ensure Safety in Industrial Applications
-

Exploring the Future of Stainless Ball Valves at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-
Unlocking the Efficiency of Cryogenic Solenoid Valves: A Deep Dive into Their Applications and Performance Data
-

Top 10 Check Valve Types for Optimal Flow Control and Industry Applications
-

The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Right Flow Check Valve for Your System Needs
