What is a Cryogenic Valve and How Does it Work?
Cryogenic valves are essential devices in managing extremely low temperatures in various industries. These valves control the flow of cryogenic liquids like liquid nitrogen and helium. Dr. Sarah Thompson, a leading expert in cryogenic technology, once said, "Cryogenic valves are the unsung heroes of modern engineering." Her insights emphasize their critical role in sectors like aerospace and medical applications.
Understanding how cryogenic valves function is vital. These valves must withstand severe temperatures while ensuring reliable performance. Often, with advancements, the design can pose challenges for manufacturers. This creates opportunities for innovation, yet many products still face setbacks in quality control. The industry often looks for new materials that perform better under cryogenic conditions, which begs the question: Are we doing enough?
The complexity of cryogenic systems requires deep expertise. Despite the progress made, issues such as leakage and efficiency remain common concerns. Continuous improvements are necessary. As industries evolve, the role of cryogenic valves will be even more significant, making the exploration of their design and function crucial to our future.
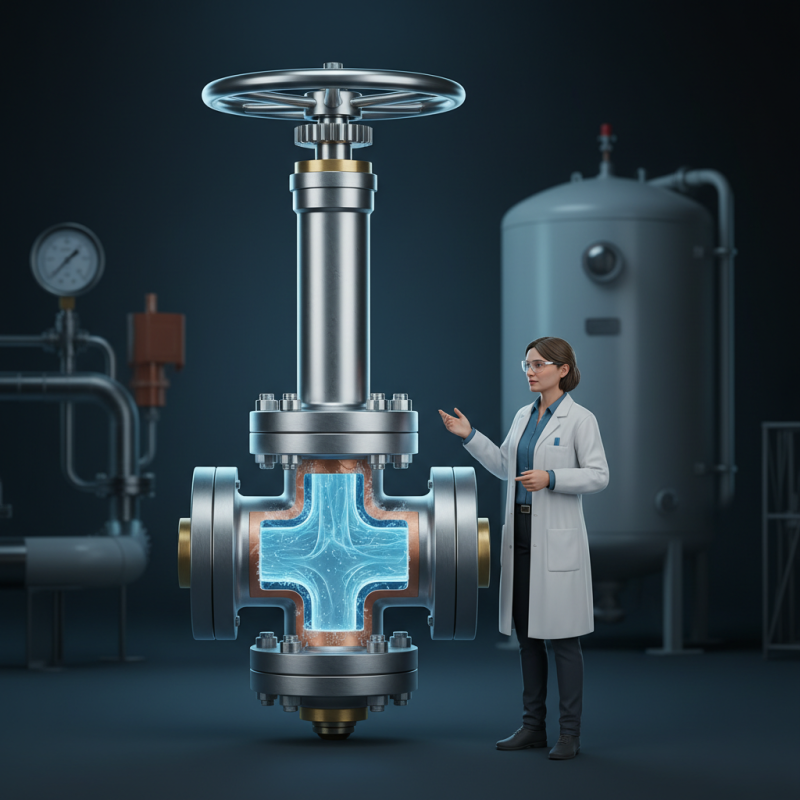

What is a Cryogenic Valve? Definition and Applications in Industry
A cryogenic valve plays a crucial role in various industries, especially where extremely low temperatures are involved.
These valves manage the flow of gases and liquids at temperatures typically below -150°C (-238°F).
Their primary function is to ensure safety and efficiency
when dealing with liquefied gases such as LNG or helium.
In industrial applications, cryogenic valves are used in sectors like aerospace, medical, and natural gas.
For instance, the global cryogenic valve market is projected to reach approximately $6.2 billion by 2027,
driven by the increasing demand for liquefied natural gas. These valves must withstand
significant pressure variations and thermal stresses. They are designed with specialized materials to resist
damage from extreme temperatures.
Tips:
When selecting cryogenic valves, consider the material and sealing method. A good seal is vital for
preventing leaks. Regular maintenance is necessary to ensure optimal performance.
Despite the advances in cryogenic technology, occasional failures occur.
Valves may not fully seal under pressure, leading to leaks that can compromise safety.
Additionally, installation errors can result in inefficiencies.
A thorough evaluation before installation is essential to mitigate these risks.
Understanding the working principles of cryogenic valves can help in avoiding costly mistakes.
The Functionality of Cryogenic Valves: Mechanism Explained
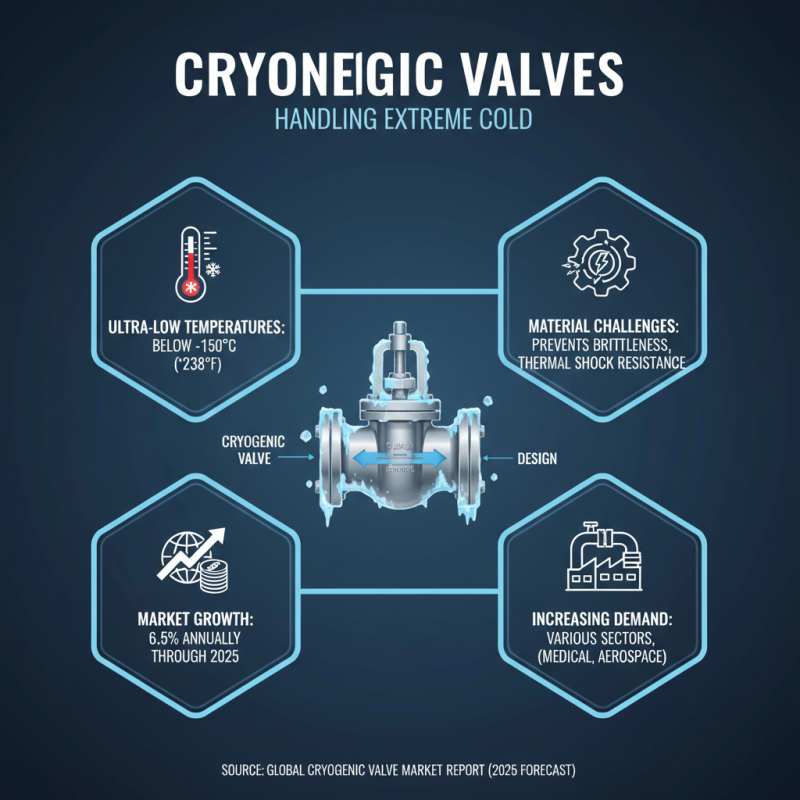
Cryogenic valves play a crucial role in handling liquefied gases at extremely low temperatures. These temperatures often reach below -150°C (-238°F), where ordinary materials may become brittle. The structure of cryogenic valves must withstand severe thermal shocks. A recent report by the Global Cryogenic Valve Market forecasted that the industry will grow by about 6.5% annually through 2025. This underscores the increasing demand for effective cryogenic systems in various sectors.
The operation of cryogenic valves relies on precise mechanisms. A common design includes a stem that opens and closes the valve seat. This action regulates the flow of gases. Some designs feature a bellows to prevent leakage at low temperatures. Other references indicate the necessity for rigorous testing under extreme conditions. Experts suggest that even a minor flaw can lead to catastrophic failures and safety hazards. Thus, constant innovation in materials and designs is essential.
Moreover, the maintenance of these valves often requires specialized knowledge. Technicians must be trained to work with the unique challenges presented by cryogenic systems. Failure to observe proper protocols may lead to decreased efficiency. Industry statistics show that nearly 30% of operational failures in cryogenic systems stem from valve malfunctions. Addressing these issues through advanced training is crucial for operational safety and reliability.
Key Materials Used in Cryogenic Valve Construction

When discussing cryogenic valves, one cannot overlook the significance of the materials used in their construction. Cryogenic applications require components that can withstand extremely low temperatures. Common materials include stainless steel, which provides strength and corrosion resistance. Additionally, special alloys such as Inconel offer exceptional performance in harsh environments.
Another critical material choice is Teflon, known for its low friction properties. This material helps ensure smooth valve operation under cold conditions. Rubber seals, often made from fluoropolymer, are essential. They provide flexibility while maintaining integrity at cryogenic temperatures. However, finding the right balance between strength and temperature resistance can be challenging. Engineers must test these materials under varied conditions.
To complicate matters, some materials perform well at low temperatures but fail under pressure. This need for careful selection often leads to trial and error. Engineers might repeat tests to find the perfect mix. Understanding these materials' limitations is crucial. It requires constant evaluation and adaptation.
Performance Metrics: Operating Temperature Ranges and Pressure Ratings
Cryogenic valves play a crucial role in handling extremely low temperatures. They are designed to operate effectively in conditions where temperatures drop below -150 degrees Celsius. This poses unique challenges. The materials used must withstand intense cold without becoming brittle or breaking.
Pressure ratings vary significantly among different models. Some may withstand pressures up to 1000 psi, while others are rated for lower limits. Choosing the right valve is not straightforward. It often requires a deep understanding of the specific application. Overlooking these metrics can lead to system inefficiencies. The consequences can be severe in critical applications, resulting in costly downtime or even safety issues.
Maintenance and Safety Considerations for Cryogenic Valves in Operation
Cryogenic valves are critical in systems handling liquefied gases, such as natural gas. However, their operation requires specific maintenance and safety protocols. A recent industry report indicates that regular inspections can reduce valve failures by up to 30%. Implementing routine maintenance checks ensures these valves function properly, preventing costly downtimes.
Safety is another pressing concern. Cryogenic fluids can cause severe frostbite and other hazards. Proper training for personnel is essential. In fact, studies show that proper training can decrease workplace incidents by 25%. Protective equipment, like insulated gloves and face shields, is also crucial. Even small lapses in safety can lead to significant risks.
The environment where these valves operate can be harsh. Factors like temperature fluctuations and pressure surges contribute to wear. Monitoring systems can help track these conditions. Yet, reliance on technology alone is not enough. Regular audits and hands-on assessments are vital. Ignoring these practices can lead to failures that might have been preventable.
Cryogenic Valve Performance Data
This bar chart displays the operational efficiency of various types of cryogenic valves. The data suggests that Valve Type A has the highest efficiency, while Valve Type C demonstrates the lowest. Understanding these performance metrics is crucial for maintenance and safety considerations in cryogenic valve operations.
Related Posts
-
How to Choose the Right Cryogenic Valves for Your Applications
-
Unlocking the Science Behind Cryogenic Valves: Essential Insights for Safe Operation
-

The Essential Role of Cryogenic Valves in Modern Cryogenic Systems and Their Impact on Energy Efficiency
-

10 Expert Tips for Choosing the Right Liquid Nitrogen Valve for Your Needs
-
Best Cryogenic Check Valves for Essential Applications in Cold Environments
-

What is a Pressure Control Valve and How Does It Work in Different Applications
