What is an Electronic Valve and How Does it Work in Modern Systems
The increasing complexity and efficiency demands of modern systems have led to significant advancements in control technologies, particularly in the field of fluid and gas management. Among these innovations, the electronic valve plays a pivotal role, offering unmatched precision in regulating flow and pressure. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the electronic valve market is projected to reach $34.6 billion by 2025, highlighting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 6.5% from 2020 to 2025. This growth is driven by the rising need for automation across various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, and HVAC systems.
Electronic valves leverage advanced technologies such as sensors and microcontrollers to operate fluid control systems with enhanced responsiveness and reliability. Their ability to provide real-time data and remote controlled functionality not only boosts operational efficiency but also contributes to energy conservation within industrial processes. Industry analysts emphasize that the integration of electronic valves into system processes can reduce energy consumption by up to 20%, significantly impacting sustainability efforts and operational costs. As sectors continue to evolve and adopt smart technologies, understanding how electronic valves work and their applications remains crucial for professionals aiming to optimize fluid management systems and enhance overall productivity.
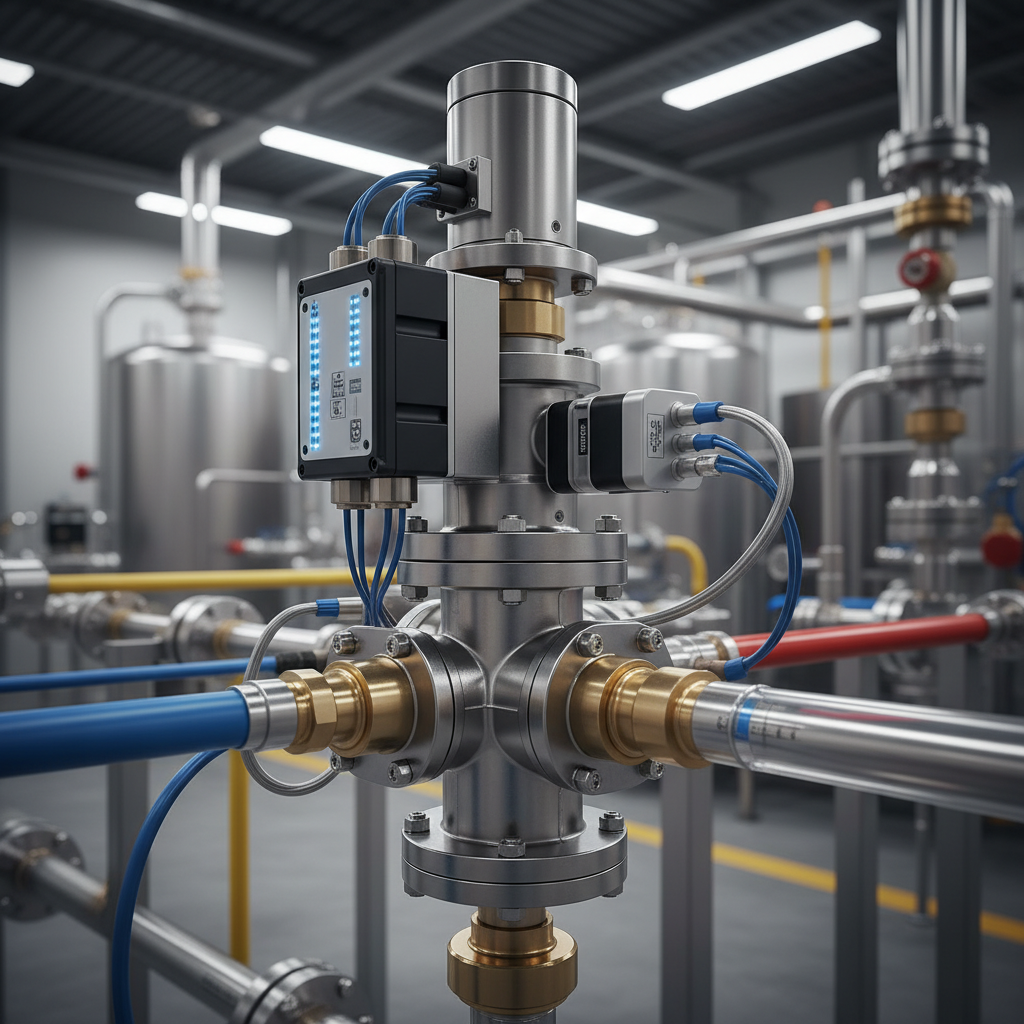

Definition and Basic Function of Electronic Valves

Electronic valves are critical components in contemporary systems, serving as automated mechanisms for controlling fluid flow, pressure, and temperature within various applications. These devices leverage electronic signals to regulate the opening and closing of valves, offering enhanced precision and responsiveness compared to traditional mechanical valves.
According to the Global Electronic Valve Market report, the industry is expected to grow at a CAGR of over 5% through 2027, indicating increasing adoption in sectors such as automotive, manufacturing, and HVAC systems.
The basic function of electronic valves involves converting electrical energy into mechanical motion, which in turn adjusts the valve position to manage fluid passage. This capability not only enhances operational efficiency but also facilitates advanced features like remote monitoring and integration with automated control systems. In a study by Research and Markets, it was noted that over 60% of modern manufacturing facilities are now implementing electronic valve solutions to improve their process automation and reduce energy consumption. As industries continue to innovate, the demand for electronic valves is poised to expand, driven by their vital role in modern automation technologies.
Types of Electronic Valves Used in Modern Systems
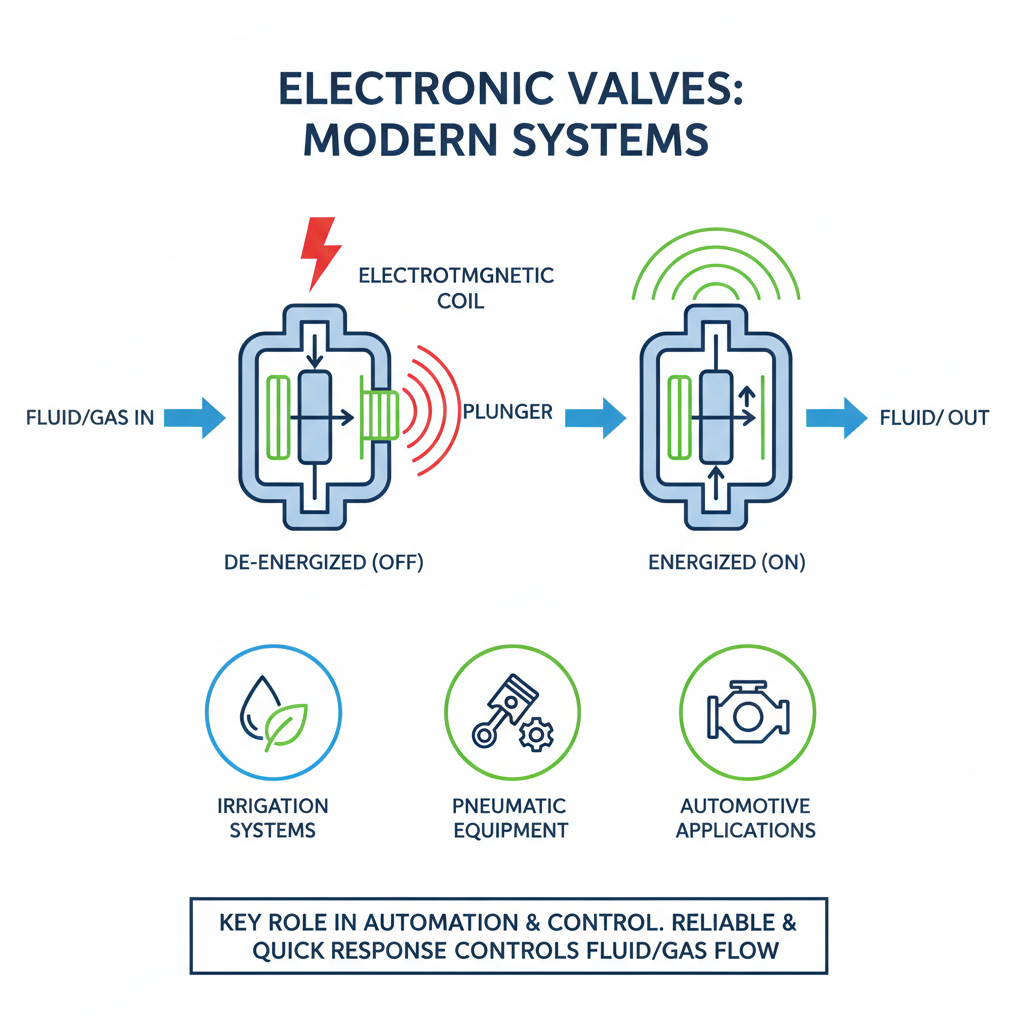
Electronic valves play a crucial role in modern systems, serving as vital components in various applications, such as automation and control. One of the most common types is the solenoid valve, which uses an electromagnetic coil to control the flow of fluids or gases. When electricity is applied, the coil generates a magnetic field that moves a plunger, allowing or blocking the passage of the medium. Solenoid valves are widely used in irrigation systems, pneumatic equipment, and even in automotive applications due to their reliability and quick response times.
Another significant type of electronic valve is the proportional valve, which adjusts the flow rate or pressure based on electrical signals. These valves enable finer control in systems where precise fluid dynamics are essential, such as in hydraulic machinery or advanced manufacturing processes. The proportional valves can be controlled through various signal types, including analog or digital inputs, making them versatile for different types of modern systems. The accurate modulation they provide enhances efficiency and performance, particularly in complex systems requiring adaptive responses.
Principles of Operation for Electronic Valves
Electronic valves, often referred to as solenoid valves or electronic control valves, play a crucial role in modern systems by regulating the flow of fluids or gases with precision. The principles of operation for electronic valves are primarily based on electromagnetic principles, where an electric current is used to control the opening and closing of the valve mechanism. When an electrical signal is applied to the coil of the solenoid, it generates a magnetic field that either pulls or pushes a plunger within the valve body, modifying the flow path based on the desired action.
This actuation method allows for rapid and accurate control of flow, often managed by advanced control systems such as programmable logic controllers (PLCs) or computerized automation systems. Electronic valves can be designed to operate in various configurations, including normally closed or normally open states, enhancing their versatility in applications ranging from HVAC systems to industrial automation. Furthermore, modern electronic valves often integrate sensors and feedback mechanisms to provide real-time data and improved responsiveness, leading to more efficient and reliable system operations.
What is an Electronic Valve and How Does it Work in Modern Systems - Principles of Operation for Electronic Valves
| Feature | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Electromagnetic, Solenoid, and Motorized | HVAC systems, Automotive, Industrial automation |
| Control Signal | Analog or Digital | Robotic systems, Process control systems |
| Power Source | DC, AC, or Battery operated | Entertainment systems, Smart home devices |
| Operation Cycle | Open/Close or Variable Control | Water management systems, Agricultural systems |
| Benefits | High precision, Reduced wear and tear, Energy efficiency | Manufacturing, Aerospace |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance requirements with proper installation | Facility management, Utility services |
Applications of Electronic Valves in Various Industries
Electronic valves play a crucial role across various industries by providing precise control over fluid and gas flow. The applications of these valves are diverse, ranging from automotive systems to HVAC and industrial automation. In HVAC systems, electronic expansion valves ensure efficient temperature regulation, enhancing energy savings and comfort in commercial and residential buildings. Additionally, in the automotive sector, electronic valves contribute to improved fuel efficiency and performance by precisely managing fuel and air mixtures.
The market for electronic valves is witnessing significant growth. For instance, the electronic expansion valves market is anticipated to reach USD 1986.0 billion by 2035, driven by advancements in technology and increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions. Furthermore, the valve remote control system market is projected to grow at a robust rate due to heightened safety standards and remote operation requirements in industrial processes. As industries continue to seek innovative solutions, the integration of electronic valves will undoubtedly become more prevalent, revolutionizing how fluids and gases are managed in modern systems.
Applications of Electronic Valves in Various Industries
This chart illustrates the percentage usage of electronic valves across various industries. The automotive industry leads with 35%, showcasing the significant role of electronic valves in modern vehicles. Healthcare follows with 25%, reflecting the importance of precision in medical devices. Manufacturing and water management utilize electronic valves at 20% and 10%, respectively, while HVAC systems also account for 10%, highlighting their versatility in regulating environments.
Advantages of Using Electronic Valves Over Mechanical Ones
Electronic valves represent a significant innovation over traditional mechanical valves, particularly in modern automated systems. One of the key advantages is their precision in control. According to a report by Research and Markets, the global market for electronic valves is projected to grow by over 8% annually, driven largely by the need for enhanced efficiency in industrial applications. Electronic valves can adjust flow rates and pressure with high accuracy, minimizing waste and energy consumption, which is essential for industries aiming to meet stringent environmental regulations.
Furthermore, the reliability and longevity of electronic valves contribute to their growing popularity. A study published by the International Journal of Industrial Automation revealed that electronic valves have a failure rate that is 40% lower than their mechanical counterparts. This increased durability not only reduces maintenance costs but also ensures consistent operation in harsh environments.
As industries increasingly focus on automation and IoT integration, the demand for electronic valves is expected to rise, reflecting their pivotal role in improving system performance and operational efficiency.
Related Posts
-
Essential Guide to Understanding High Pressure Relief Valves: How They Ensure Safety in Industrial Applications
-

Exploring the Future of Stainless Ball Valves at the 138th China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

Innovative Trends in Low Pressure Relief Valves at the 2025 China Import and Export Fair
-

Understanding the Importance of Control Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

Unlocking Opportunities for Vacuum Check Valves at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 in China
-
Unlocking the Efficiency of Cryogenic Solenoid Valves: A Deep Dive into Their Applications and Performance Data
