What is a Pressure Control Valve and How Does It Work in Different Applications
A pressure control valve (PCV) is a vital component in various engineering systems, responsible for maintaining the desired pressure levels within a fluid system. Its primary function is to automatically regulate the pressure of gases or liquids, ensuring optimal performance and safety in diverse applications, from industrial processes to residential plumbing. By adjusting the flow rate based on pressure readings, these valves play a crucial role in preventing equipment damage, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring the overall reliability of fluid systems.
In numerous applications, such as manufacturing, automotive, and HVAC systems, the pressure control valve is essential for managing pressure fluctuations and maintaining stability. It operates by responding to changes in the system, providing real-time regulation that enhances operational efficiency. Understanding how these valves function and their specific roles in different contexts is key for engineers and technicians alike, as it helps in the design, implementation, and maintenance of effective fluid control systems. This article explores the fundamental principles behind pressure control valves, their various types, and the critical roles they play across multiple industries.
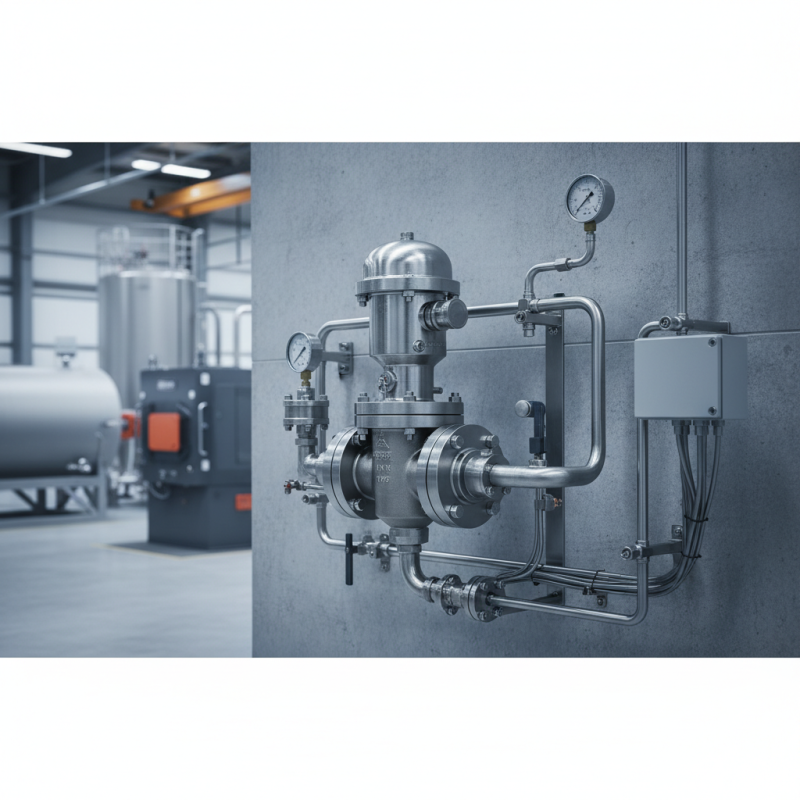

What is a Pressure Control Valve?
A pressure control valve is a critical component in various fluid systems, designed to regulate and maintain the desired pressure within a system. It functions by automatically adjusting the flow of fluids, whether they are gases or liquids, to ensure that pressure levels remain within specified limits. Typically installed in pipes or vessels, these valves are essential for preventing overpressure situations, which can lead to system failures or potential hazards.
The operation of a pressure control valve is based on the principle of feedback control. When the pressure in the system exceeds the pre-set threshold, the valve responds by throttling or fully opening to relieve excess pressure. Conversely, if the pressure drops below the desired level, the valve adjusts to restrict flow, allowing the pressure to build back up. This dynamic response is crucial for maintaining system stability in applications such as water distribution, oil refining, and chemical processing, where precise pressure management is vital for operational efficiency and safety.
Key Components of a Pressure Control Valve
A pressure control valve (PCV) is essential in various industrial applications where maintaining desired pressure levels is crucial for system efficiency and safety. Key components of a pressure control valve include the body, actuator, spring, and sensing element. The body houses the internal mechanisms of the valve, enabling it to regulate fluid flow. The actuator responds to the pressure signals received from the sensing element, which monitors the pressure within the system. The spring provides the necessary force to return the valve to its original position once the pressure stabilizes.
In a report by the International Society of Automation (ISA), it was noted that effective pressure control mechanisms can enhance process efficiency by up to 25% in certain industries. The spring-loaded design commonly found in PCVs is notable for its reliability and responsiveness, allowing for immediate adjustments in response to fluctuating system pressures. Moreover, with advancements in technology, electronic pressure control valves featuring digital actuators are becoming increasingly popular, providing more precise control and reducing energy consumption by optimizing flow conditions based on real-time data. These developments signify the vital role that the components of pressure control valves play in modern engineering practices, ensuring systems function smoothly across a range of applications, from water treatment to chemical processing.
Mechanism of Operation in Pressure Regulation
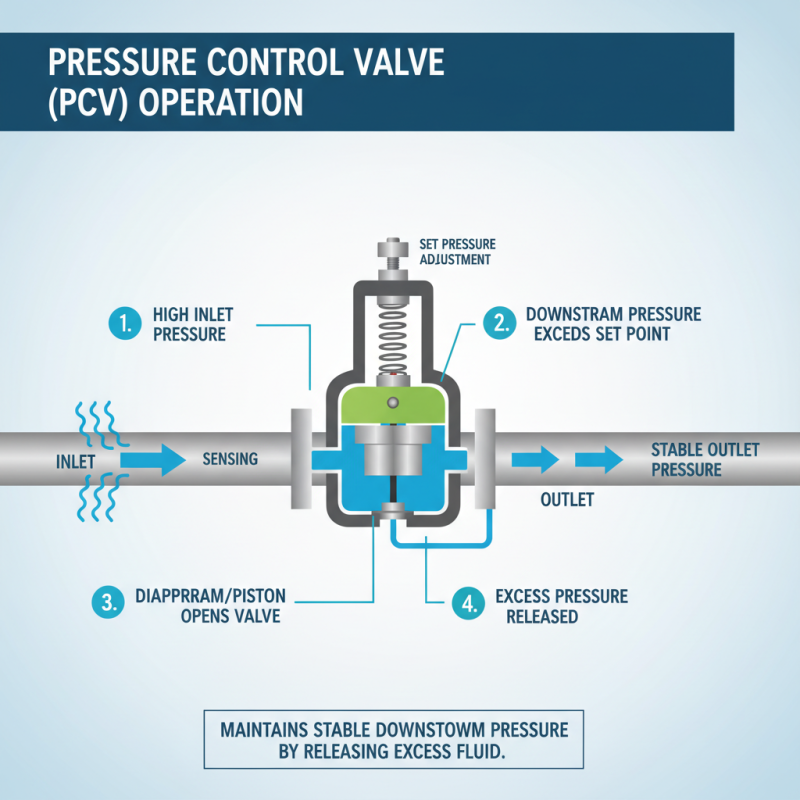
A pressure control valve (PCV) plays a crucial role in various systems by regulating the pressure of fluids within a pipeline. The mechanism of operation revolves around maintaining a specific pressure level, which is essential for the efficiency and safety of fluid handling processes. Typically, the valve utilizes a spring-loaded diaphragm or piston that responds to changes in downstream pressure. When the pressure exceeds a predetermined set point, the diaphragm or piston moves, allowing the valve to open and release excess pressure, thereby stabilizing the system.
In different applications, such as water treatment, oil refineries, and HVAC systems, the PCV adapts to varying fluid dynamics. In water systems, for instance, it ensures that pressure levels remain optimal to prevent pipe bursts, while in industrial settings, it maintains consistent pressure for process control. The precise adjustment of the valve is critical; too much pressure can lead to equipment failure, whereas too little can disrupt operational efficiency. By utilizing feedback mechanisms and sensors, modern pressure control valves can provide enhanced responsiveness and automation, ensuring effective pressure regulation across diverse operational requirements.
Applications of Pressure Control Valves in Various Industries
Pressure control valves (PCVs) play a critical role across various industries by regulating fluid pressure within systems, ensuring optimal performance and safety. In the oil and gas sector, for example, systems face significant pressure fluctuations that can lead to leaks or system failures. According to a report by the International Energy Agency, efficient pressure management can reduce operational risks by up to 30%. PCVs are essential in maintaining pressure levels within the operational limits of pipelines and storage tanks, thus protecting infrastructure and personnel.
In the manufacturing industry, pressure control valves are pivotal for processes involving hydraulic and pneumatic systems. A study conducted by the American Society for Mechanical Engineers highlighted that precise pressure control can enhance operational efficiency by approximately 25%. For instance, in automotive manufacturing, PCVs are utilized in assembly lines to maintain consistent pressure in hydraulic presses, which are critical for stamping and forming components. This controlled environment not only improves product quality but also reduces resource wastage, illustrating the valve's significance in economic sustainability and production efficiency.
Advantages and Limitations of Pressure Control Valves
Pressure control valves (PCVs) play a critical role in maintaining safe and optimal operating conditions across various industries by regulating fluid pressure in systems. One key advantage of PCVs is their ability to enhance system efficiency. By precisely maintaining the desired pressure levels, they help prevent energy loss, which is crucial in systems where energy costs represent a significant portion of operational expenses. According to a 2022 report by the International Society of Automation, optimizing pressure control can lead to energy savings of 15-20% in industrial applications.
However, PCVs also come with limitations. One notable drawback is their susceptibility to wear and tear over time, particularly in high-pressure or corrosive environments. Regular maintenance and monitoring are essential to ensure their optimal performance; failure to maintain them can lead to costly downtimes or even catastrophic system failures. The National Fluid Power Association highlights that incorrect installation or maintenance of pressure control valves is responsible for nearly 30% of hydraulic system failures.
Tip: Regularly inspect and calibrate your pressure control valves to mitigate risks associated with wear and enhance system longevity.
Additionally, while PCVs can greatly improve safety by preventing overpressure conditions, they may not be suitable for all applications. In scenarios where rapid pressure fluctuations are anticipated, a more dynamic control solution may be required. Understanding your specific system requirements is crucial for selecting the appropriate device for effective pressure management.
Tip: Consider the operational environment and fluid characteristics when choosing a pressure control valve to ensure optimal compatibility and performance.
Related Posts
-

Understanding the Essential Role of Pressure Vacuum Valves in Modern Industrial Systems
-

Understanding the Importance of Relief Valves in Modern Industrial Applications
-

Top 10 Types of Valves: Unlocking Key Insights for Industrial Efficiency
-
Why Choosing Stainless Ball Valves is Essential for Your Industrial Applications
-

Understanding the Benefits of Choosing Stainless Ball Valves for Your Plumbing Needs
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Flow Check Valves in Your Plumbing System
